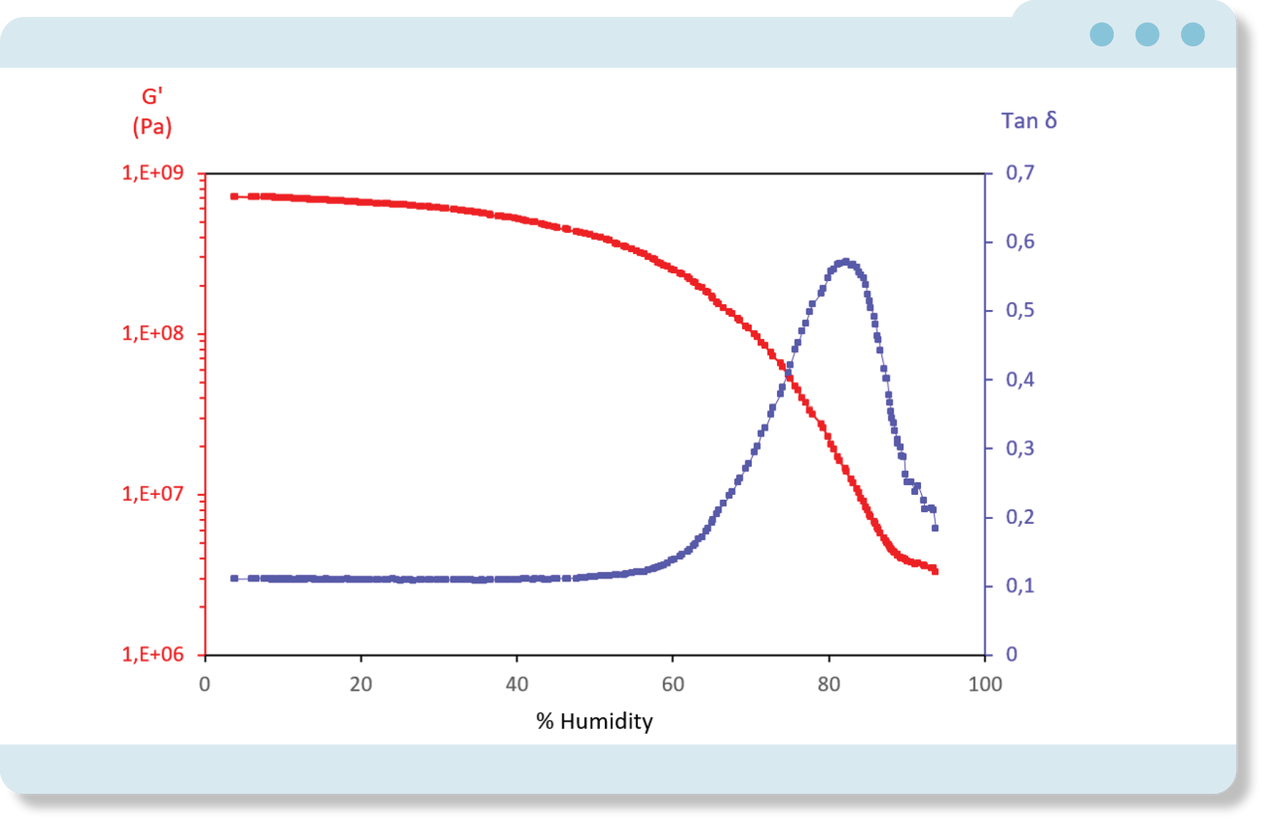
Effect of relative humidity on chitosan polymer
Water-sensitive materials can be tested at controlled humidity using a dedicated humidity module. The example of chitosan, a biodegradable polymer, exposed to increasing humidity shows the drastic impact of water on the polymer’s structure and viscoelastic properties: the shear modulus decreases by a factor of 100 at 90% RH, while Delta Tan reaches a maximum value at 80% RH.
Additional accessories enable the specimen to be immersed in liquids during the test.